Belly fat, also known as visceral fat, is the fat that accumulates around your abdominal organs. Unlike subcutaneous fat, which sits just beneath the skin, visceral fat is more metabolically active and has been linked to an increased risk of several chronic diseases, including:
Diseases From Belly Fat
Heart disease

Belly fat is a major risk factor for heart disease, the leading cause of death worldwide. Visceral fat releases hormones and inflammatory substances that can damage your blood vessels and increase your risk of heart attack and stroke. As per the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), the number of fatalities due to heart attacks in 2022 surged by 12.5%, totaling 32,457 deaths, compared to the preceding year. Additionally, there was a 10.1% increase in sudden deaths, totaling 56,450, with a significant portion attributed to heart attacks.
Type 2 diabetes
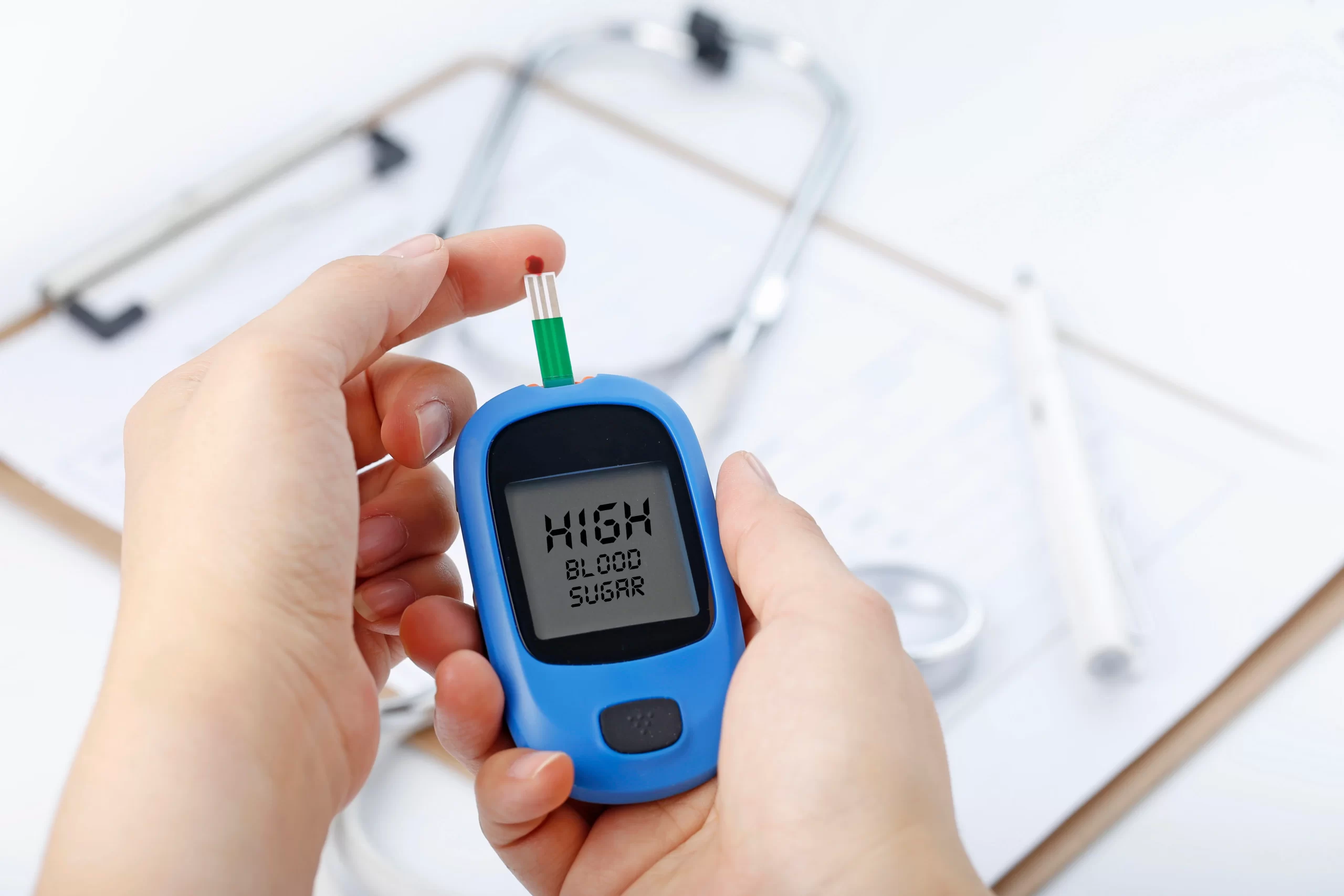
Belly fat can impair your body’s ability to use insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. This can lead to insulin resistance and eventually type 2 diabetes. As reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the annual death toll from diabetes in the United States stands at 79,535. In 2021, diabetes affected 38.4 million Americans, constituting 11.6% of the population, with 29.7 million diagnosed cases and 8.7 million undiagnosed cases.
Some cancers
Belly fat has been linked to an increased risk of certain cancers, including colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer, and breast cancer.
Sleep apnea
Belly fat can put pressure on your diaphragm, making it harder to breathe at night and increasing your risk of sleep apnea. As per the American Sleep Apnea Association, 38,000 individuals in the United States succumb to heart disease annually, with sleep apnea complicating the condition.
Statistics on Belly Fat
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), in the United States:
- Over 40% of adults have unhealthy amounts of belly fat.
- Belly fat is more common in men than in women.
- Belly fat risk increases with age.
- A 2020 study published in the National Institutes of Health (NIH) journal Obesity found that South Asian adults tend to have higher levels of visceral fat compared to other ethnicities, even at a normal body weight according to BMI.
Effective Strategies to Lose Belly Fat

Losing belly fat can significantly improve your health and reduce your risk of chronic disease. While there is no magic bullet for belly fat loss, several evidence-based strategies can help you achieve your goals.
-
Focus on a Healthy Diet
Diet plays a crucial role in belly fat loss. Here are some key dietary changes to consider:
- Increase Soluble Fiber Intake: Soluble fiber promotes feelings of fullness and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Good sources of soluble fiber include fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains.
- Prioritize Lean Protein: Protein helps you build and maintain muscle mass, which can boost your metabolism and aid in belly fat burning. Lean protein sources include fish, poultry, beans, and lentils.
- Choose Complex Carbohydrates: Complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy and help regulate blood sugar levels. Opt for whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and oats, over refined carbohydrates like white bread and pasta.
- Limit Unhealthy Fats: Unhealthy fats, such as saturated and trans fats, can contribute to belly fat accumulation. Limit processed foods, fried foods, and fatty cuts of meat.
- Reduce Sugary Drinks and Processed Foods: Sugary drinks and processed foods are often high in calories, unhealthy fats, and added sugars, all of which can promote belly fat gain.
- Read Food Labels Carefully: Pay attention to serving sizes and ingredients lists when reading food labels. This can help you identify hidden sources of unhealthy fats, added sugars, and refined carbohydrates.
-
Prioritize Sleep
Getting enough sleep is essential for overall health and belly fat management. When you don’t get enough sleep, your body produces more of the stress hormone cortisol, which can promote belly fat storage. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
-
Manage Stress
Chronic stress can also lead to increased cortisol levels and belly fat accumulation. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, relaxation techniques, and spending time in nature.
-
Engage in Regular Exercise
Exercise is a powerful tool for belly fat loss. Here are two key types of exercise to incorporate into your routine:
- Aerobic Exercise: Aerobic exercise, also known as cardio, helps you burn calories and belly fat. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
- Strength Training: Strength training helps you build muscle mass, which can boost your metabolism and help you burn more calories at rest. Aim for strength training exercises that target all major muscle groups at least twice a week.
-
Consider Dietary Changes
Some research suggests that specific dietary approaches may be more effective for belly fat loss than others. Here are two options to consider:
- Low-Carb Diet: A low-carb diet can be more effective for belly fat loss than a low-fat diet. This approach restricts your intake of carbohydrates and emphasizes protein and healthy fats.
- Mindful Eating: Mindful eating practices can help you develop a healthier relationship with food and promote weight management. By paying attention to your hunger and fullness cues, you can avoid overeating and make more mindful food choices.
Additional Tips for Belly Fat Loss
Cook More Meals at Home
Cooking more meals at home allows you to control the ingredients and portion sizes of your meals. This can help you reduce your intake of unhealthy fats, added sugars, and processed foods, all of which can contribute to belly fat gain.
Incorporate Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting is an eating pattern that cycles between periods of eating and fasting. There are several different ways to practice intermittent fasting, but a popular method is the 16/8 method, which involves fasting for 16 hours each day and restricting your eating window to 8 hours. Studies have shown that intermittent fasting can be effective for belly fat loss.
Drink Green Tea
Green tea is a beverage loaded with beneficial antioxidants called catechins, which have been shown to boost metabolism and promote fat burning. Drinking green tea regularly may help you lose belly fat and improve your overall health.
Increase Probiotic Intake
Probiotics are live bacteria that offer numerous health benefits, including improved gut health and weight management. Studies suggest that probiotics may help reduce belly fat by promoting feelings of fullness and reducing inflammation. You can increase your probiotic intake by consuming yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and other fermented foods, or by taking probiotic supplements.
Be Patient and Consistent
Losing belly fat takes time and effort. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t see results immediately. Stick to your healthy lifestyle changes and be patient with yourself. Consistency is key to achieving your belly fat loss goals.
Conclusion
By incorporating these additional tips into your routine, you can further enhance your belly fat loss efforts and improve your overall health. Remember, a holistic approach that combines a healthy diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, stress management, and other lifestyle changes is most effective for sustainable belly fat loss and overall well-being.




[…] infections. While antibiotics and other medications play a crucial role in combating infections, a healthy diet rich in immune-boosting nutrients can be a powerful first line of […]